Abstract
Introduction: Smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM) is an asymptomatic and biologically heterogeneous clonal plasma cell disorder. A number of prognostic factors to identify patients at a higher risk of progression have been described, such as the size of the M protein, proportion of abnormal bone marrow plasma cells (BMPCs), immunoparesis and serum free light chain (FLC) k/l ratio. More recently, isotype-specific uninvolved heavy and light chain (HLC) pair suppression measured with the Hevylite assay was also associated with an increased risk of progression. Recent studies have evaluated the key prognostic impact of an increase in M-protein levels during follow-up ("evolving" pattern). However, an important limitation could be the evaluation of M-protein level variations based on serum protein electrophoresis (SPE) in patients with a small size M-spike. The aim of this study was to prospectively analyze the changes in M-protein according to SPE and HLC measurements, as well as other risk factors for progression, in patients with SMM.
Methods: Thirty patients newly diagnosed with SMM at a single institution from January 2014 through September 2017 were prospectively included in the study. For each patient, baseline levels of known prognostic factors (serum M-protein, serum and urine immunofixation, clonal BMPCs percentage, total immunoglobulins, involved/uninvolved FLC and involved/uninvolved HLC pairs) were recorded. During the follow up, M-protein level, FLC and isotype specific HLC pairs were also analyzed. Evolving change in M-protein level according to SPE was defined as ³ 10% increase within the first 6 months of diagnosis (if M-protein was ³ 30 g/L) and/or ³ 25% increase within the first 12 months (for any level of M-protein); evolving change according to HLC was defined as a ³ 10% increase in the involved pair. A sequential increase in each of three or more consecutive measurements from diagnosis was considered an evolving change regardless of its magnitude.
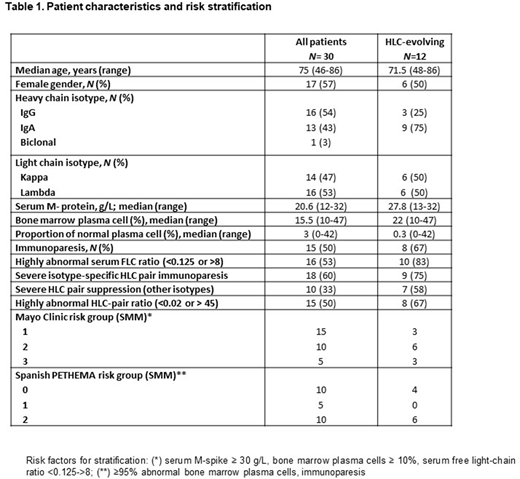
Results: The clinical characteristics of the total of patients, as well as of the patients with evolving changes in M-protein according to HLC are summarized in Table 1.
During the study period, 5/30 (17%) of patients demonstrated an evolving behavior of the M-protein according to SPE. Four of these patients (4/5) also showed a progressive increase in the M-protein in the HLC measurements. One patient showed stable HLC levels even though both the M-protein and the involved FLC progressively increased. This patient was of intermediate and low risk according to Mayo Clinic and PETHEMA scores, respectively. On follow up, no progressive suppression of the isotype-specific uninvolved HLC pair or increase in the FLC ratio was noted, and there have been no signs of progression after a follow up of 3 years.
According to involved HLC-pair levels, 12/30 (40%) of patients demonstrated an evolving behavior. Five out of 7 patients that were not classified as evolving by SPE, were IgA isotype. Eight out of 12 patients showed severe isotype-specific suppression of the uninvolved HLC-pair (> 50% below lower level of normal) as well as a highly abnormal FLC ratio (<0.125 or >8). Three out of the 4 remaining patients showed either severe isotype-specific HLC pair suppression or highly abnormal FLC ratio in follow up measurements. Compared to patients with no "HLC-evolving pattern", evolving patients were more likely to have highly abnormal FLC ratios (90 vs. 33%, p=0.009), severe suppression of the other isotypes (64 vs. 19%, p=0,024), highly abnormal isotype-specific HLC ratios (67 vs. 33%, p=NS), severe isotype-specific HLC-pair suppression (75 vs. 50%, p=NS), and immunoparesis (67 vs. 39%p=NS).
Five patients progressed to symptomatic multiple myeloma during follow up; 4 of them showed a progressive increase in the involved HLC pair from diagnosis. The remaining patient demonstrated a progressive increase in the involved HLC pair that started 19 months prior to progression, followed 4 months later with an increase in M-protein as measured by SPE.
Conclusions: In our series, the Hevylite assay allowed us to identify patients with a progressive increase in M-protein (clonal heavy/light chain pair) that was not evident with SPE measurements. This "HLC evolving pattern" was associated with other risk factors for progression to symptomatic disease and with worsening of other prognostic parameters during follow up.
Rosinol:Janssen, Celgene, Amgen, Takeda: Honoraria. Bladé:Janssen: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.